General Information
Figure 1 shows a single-lane road beam bridge that is used by not heavy vehicles.
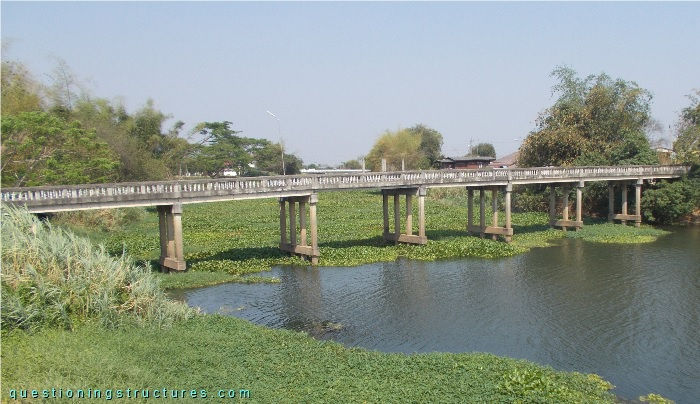

| Main span | ≅ 10 m |
| Girder | Prestressed concrete beam/reinforced concrete solid slab |
Solid Slab Sector
Figure 2 shows a schematic three-dimensional view of the bridge.
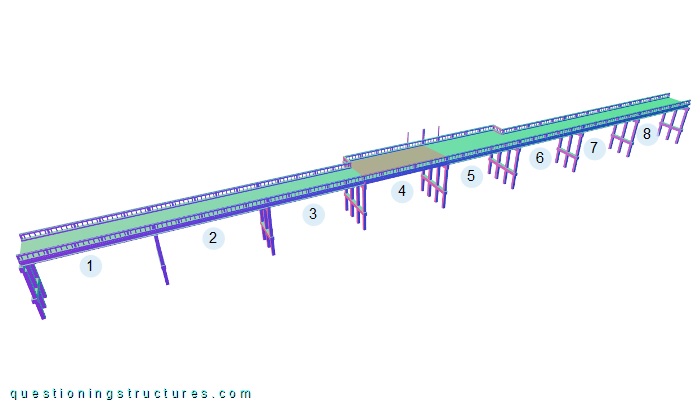
The bridge has eight equal spans and a passing place (spans 4 and 5). The girder of span 4 consists of a solid slab, while the girder of the remaining spans consists of a prestressed concrete beam. The girders are supported by three- and four-pile bents; the latter are installed in the passing place sector. Figure 3 shows the passing place sector, while figure 4 shows a side view of it.
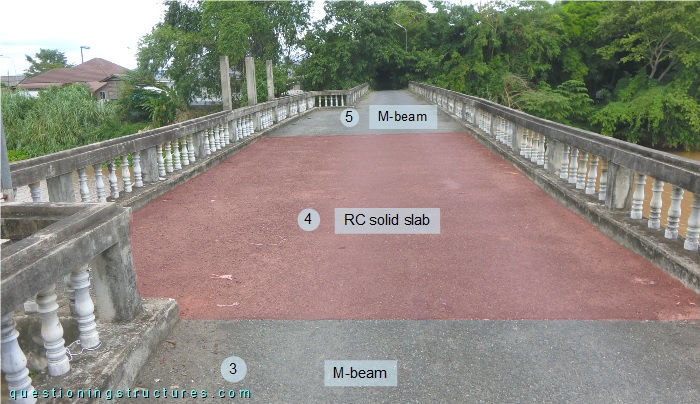
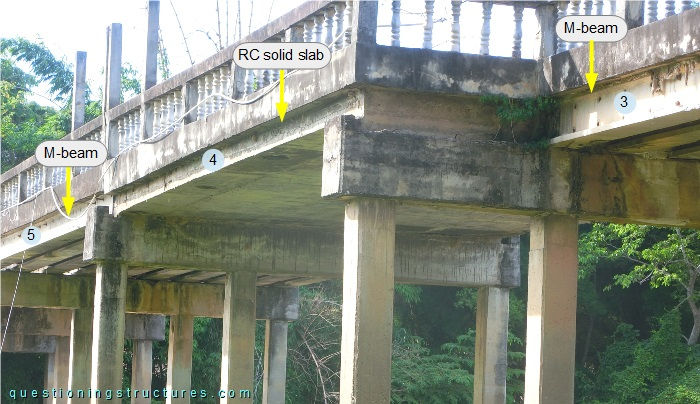


Figure 5 shows a side view of spans 3 and 4.
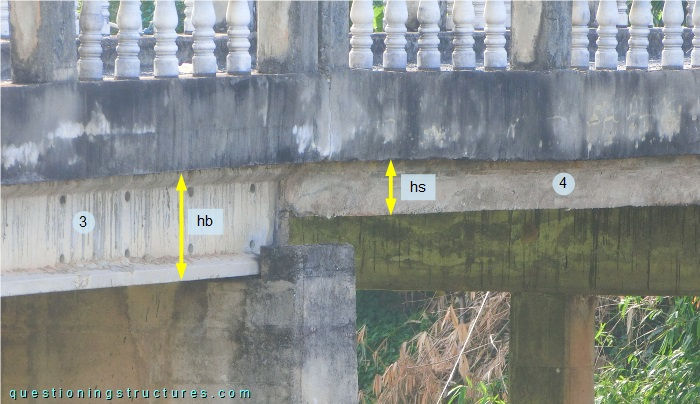

The height of the prestressed beam (hb) is greater than the thickness of the solid slab (hs).