General Information
Figure 1 shows a freestanding steel carport.
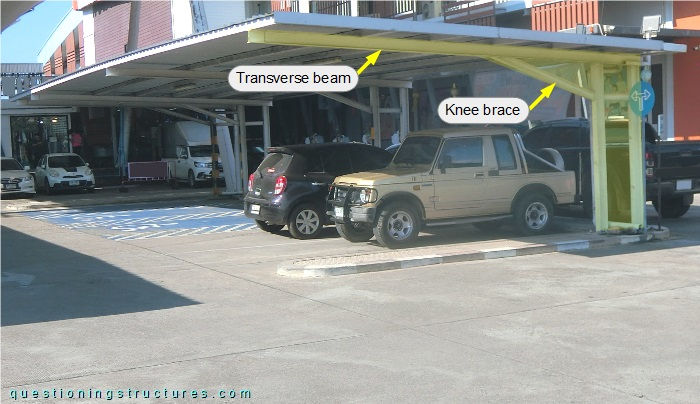

The steel structure consists mainly of columns, struts, knee braces, transverse (overhanging) beams, purlins, and metal roofing sheets. The columns, struts, knee braces, and transverse beams are made of H-sections, while the purlins are made of square hollow sections. A main unit (yellow background) consists of two columns, a strut, a knee brace, and a transverse beam.
Roof Overhang
Figure 2 shows the carport.
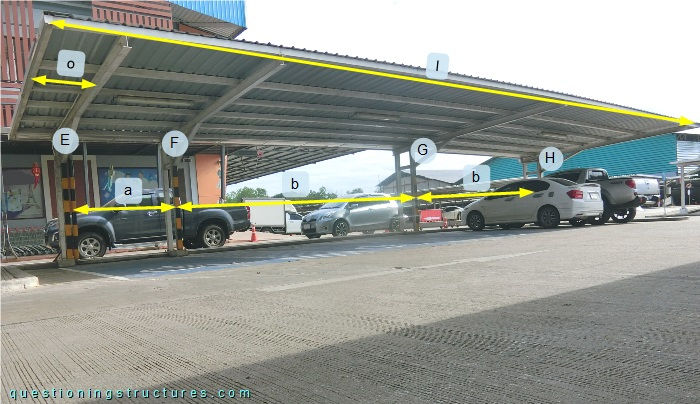

The roof length l ≅ 18 m, and the width ≅ 6 m. There are four main units (E to H) and two spacings; a ≅ 2 m, and b ≅ 7 m. The purlins overhang on both sides; the overhang o ≅ 1 m. Figure 3 shows a schematic front view of the carport and a variant without main unit E.
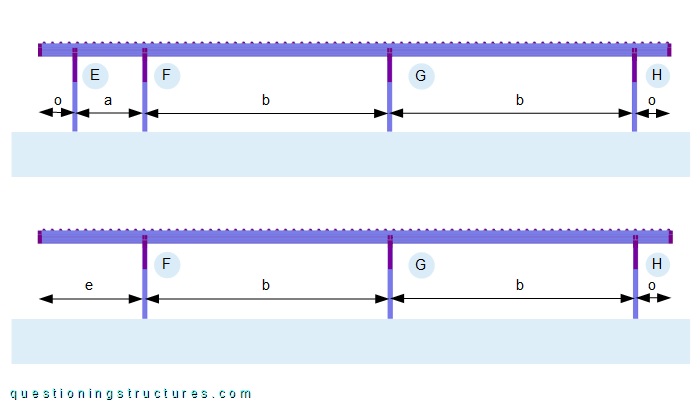
The overhang e ≅ 3 m, and the purlins are continuous over the whole roof length.
Does installing main unit E reduce the use of resources?
Columns' Bases
The columns of main units F to H have bases as shown in figure 4.
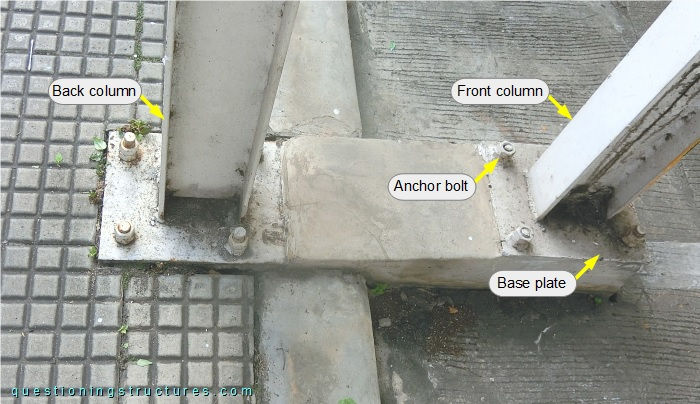
The base of each column (front and back) consists of a base plate and four anchor bolts. The columns of main unit E have bases as shown in figure 5.
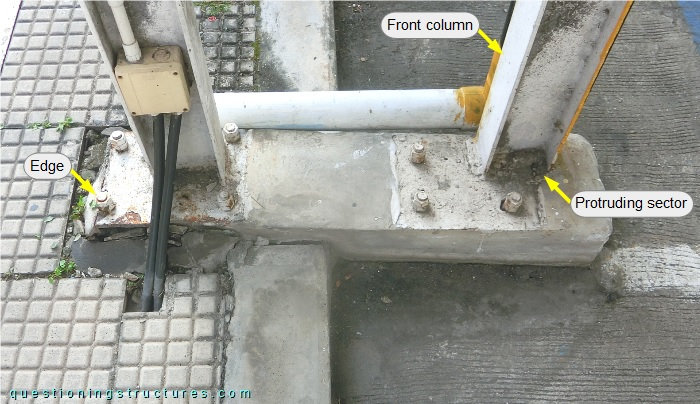

The base of the front column consists of a base plate and three anchor bolts; the column is partially outside the base plate. The base of the back column consists of a base plate and four anchor bolts, which are installed at different distances from the edges.
Does main unit E structurally behave like main unit H?