General Information
Figure 1 shows a freestanding steel carport.
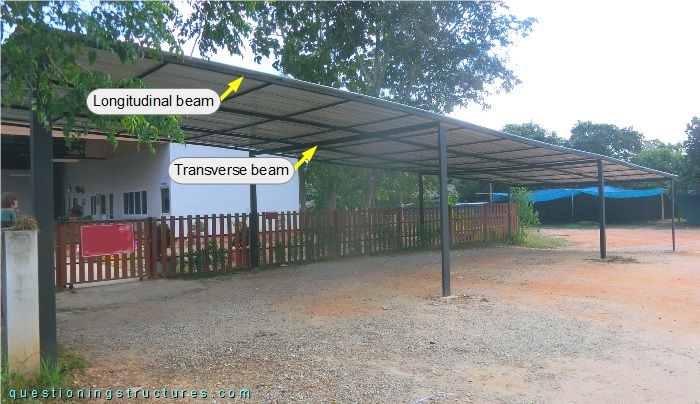

The steel structure consists mainly of columns, transverse and longitudinal beams, purlins, and metal roofing sheets. The columns are made of rectangular hollow sections, the longitudinal beams and the purlins are made of square hollow sections, and the transverse beams are made of lipped channels.
Beam Deflection
Figure 2 shows a schematic layout of the carport.
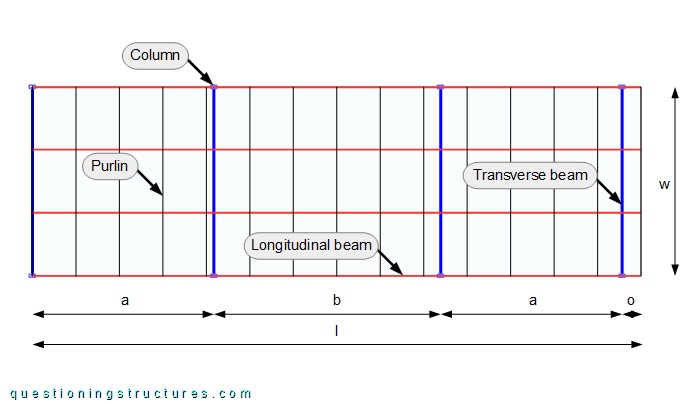
The carport length l ≅ 16.5 m, and the width w ≅ 5 m. There are four longitudinal beams; the span a ≅ 5 m, the span b ≅ 6 m, and the overhang o ≅ 0.5 m. Figure 3 shows the roof structure viewed from below.
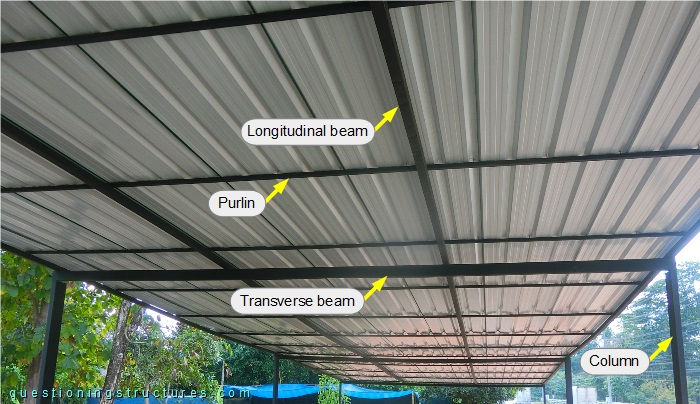

The longitudinal beams are continuous over the whole carport length and have a side length (s) of about 4 cm; that gives a main span-to-depth ratio (b/s) of 150. Figure 4 shows the column to beam connection and the beam to beam connection.

The beams are stacked directly over the column and are joined by welding. Figure 5 shows a side view of the main span region.
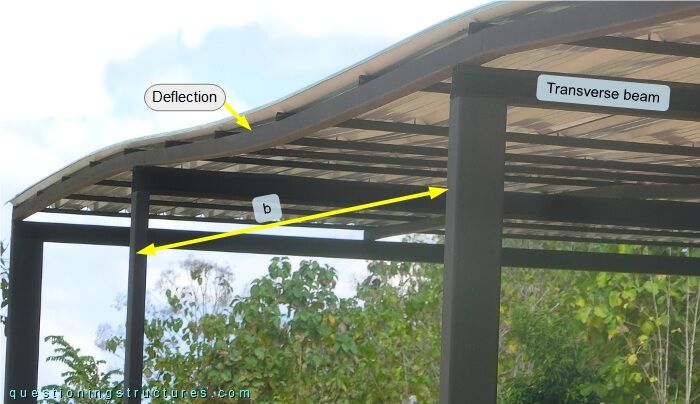

Longitudinal beam deflection is noticeable; the main span (b) deflection is about b/120.
Snowfall does not occur in the present region. Can the wind cause a structural failure?