General Information
Figure 1 shows a pedestrian suspension bridge.
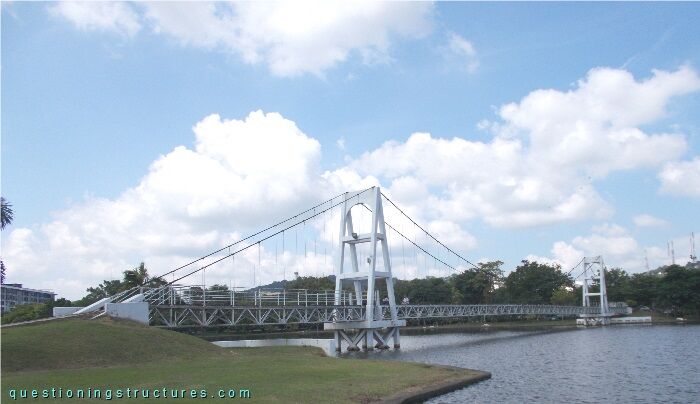

| Type | Three-span suspension bridge |
| Main span | ≅ 65 m |
| Deck width | ≅ 2 m |
| Deck width to main span ratio | ≅ 1:33 |
| Pylon | Reinforced concrete (A-type, longitudinal) |
| Girder | Steel truss |
Side Spans
Figure 2 shows a side span.
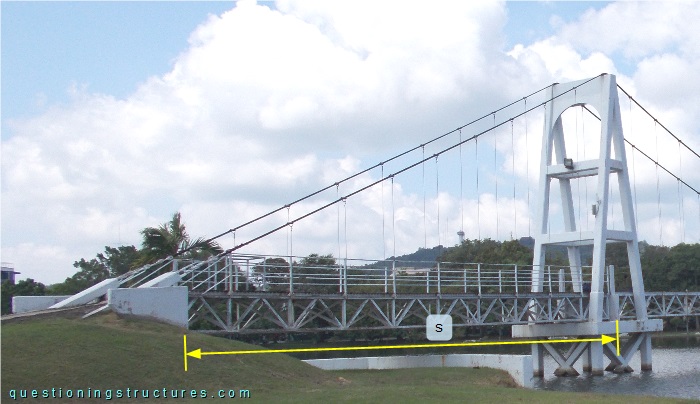

The side span s ≅ 18 m. Figure 3 shows the truss girder.
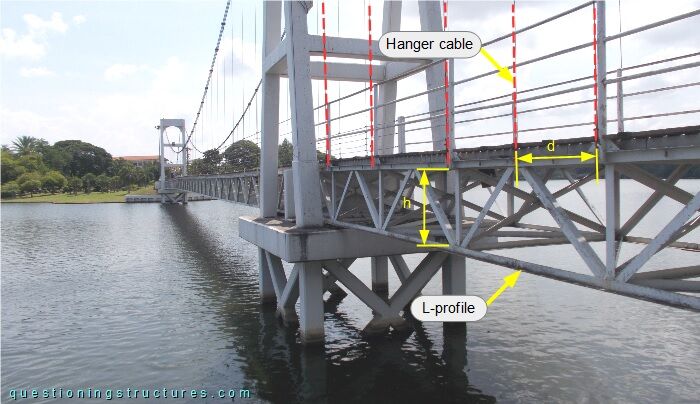
The truss girder is non-continuous, made of L-sections, and has a height (h) ≅ 0.9 m. Figure 4 shows two schematic lateral views.
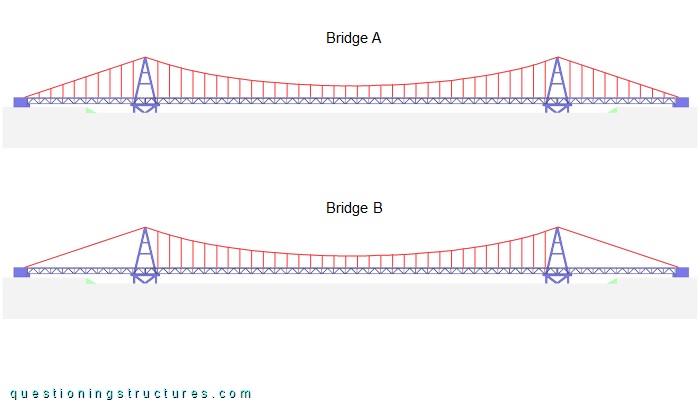
Bridge A is the above shown bridge, while bridge B is bridge A with hanger-less side spans (with two approach spans).
What are some possible reasons for choosing approach spans instead of side spans?
Side Span Hangers' Vibrations
Figure 5 shows a side span.

Video 1 shows hangers 3 and 4 during hand-induced vibration.